Getting Started
Getting Started
Section titled “Getting Started”This guide will help you add a virtual joystick to your Phaser 3 game in just a few minutes.
Visual Examples
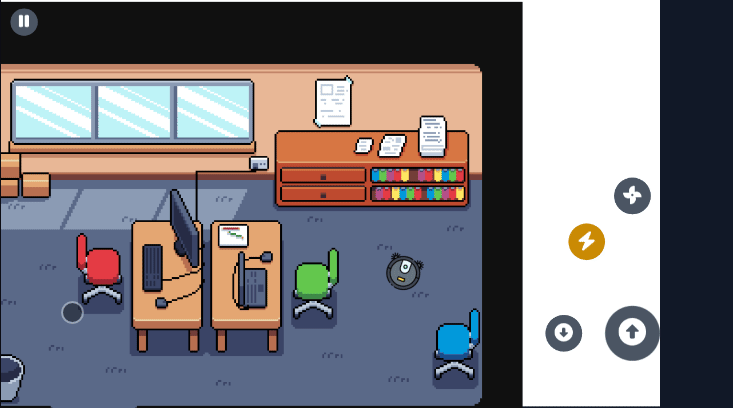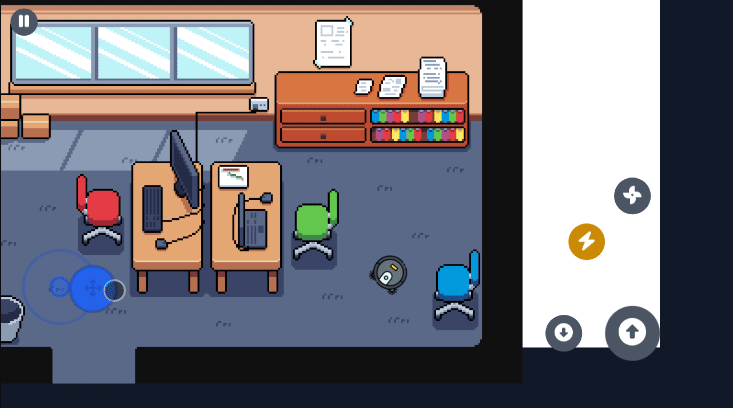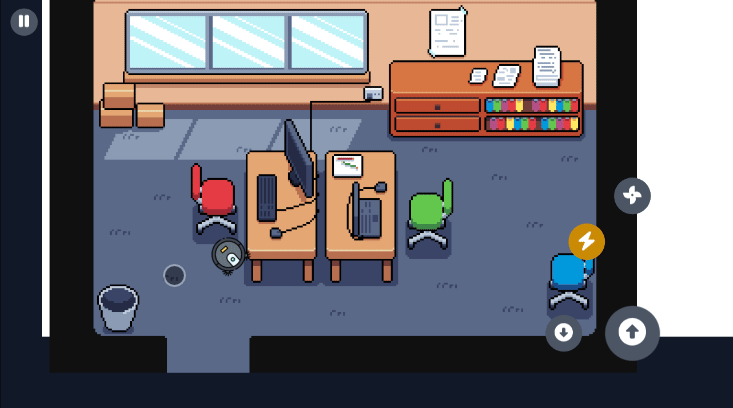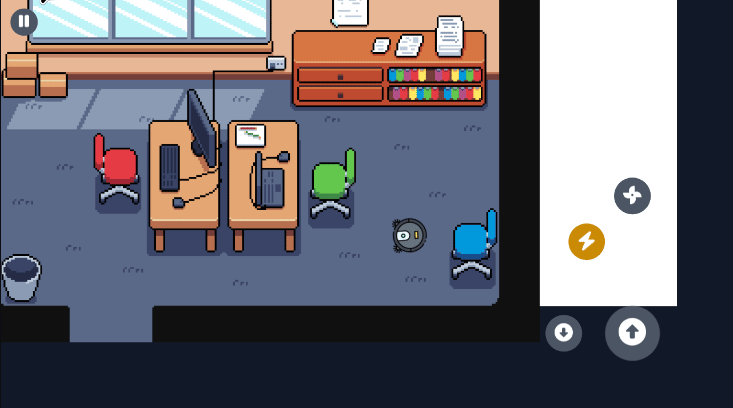
Section titled “Visual Examples”Here are some examples of the virtual joystick in action across different game genres:
Brawl Stars Style (Action Game)
Section titled “Brawl Stars Style (Action Game)”The virtual joystick provides smooth character movement with precise control, perfect for action games where quick and accurate movement is essential.
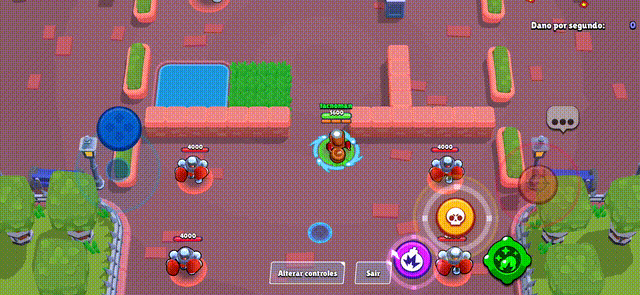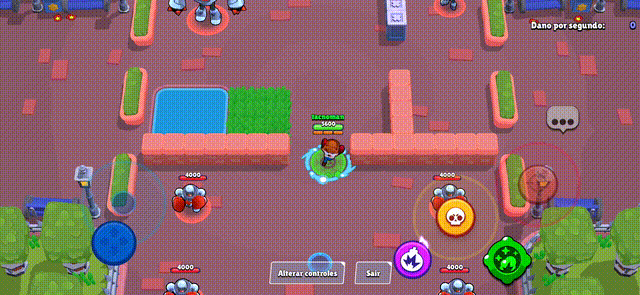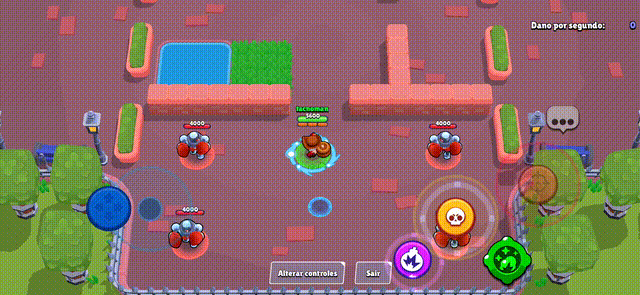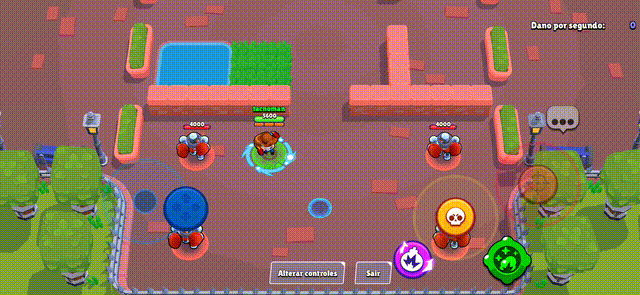
Miner Rush (Puzzle Game)
Section titled “Miner Rush (Puzzle Game)”In puzzle games like this Tetris Attack style game, the joystick offers precise control for moving pieces and navigating the game board.
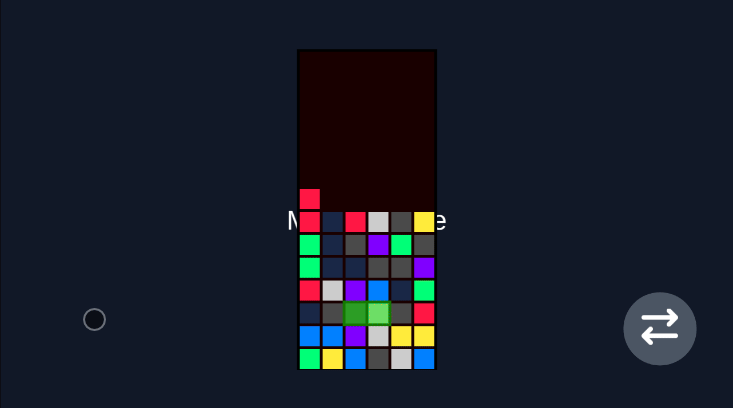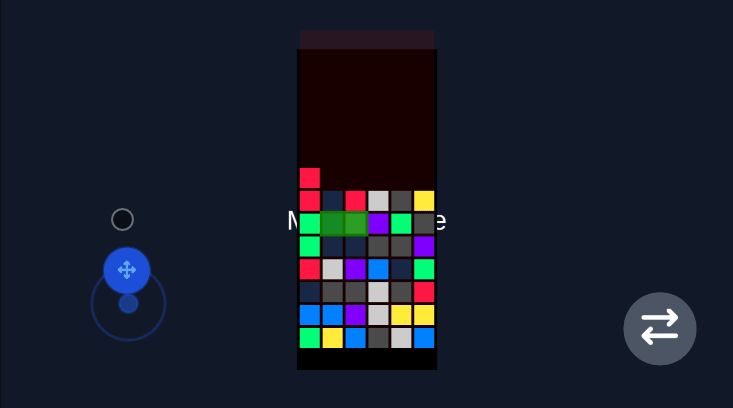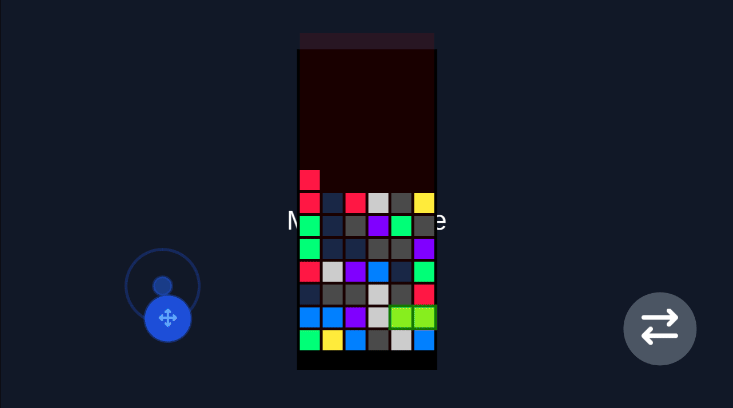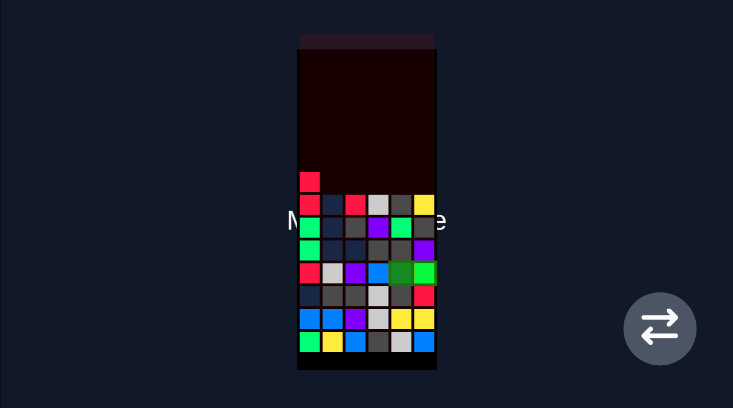
Robot Vacuum (Rotation Game)
Section titled “Robot Vacuum (Rotation Game)”For games that require rotation mechanics, the virtual joystick provides intuitive control for rotating characters or objects in any direction.
Installation
Section titled “Installation”Install the library using npm:
npm install phaser-virtual-joystick# oryarn add phaser-virtual-joystick# orpnpm add phaser-virtual-joystickBasic Setup
Section titled “Basic Setup”1. Import the Library
Section titled “1. Import the Library”import { VirtualJoystick } from 'phaser-virtual-joystick';2. Create the Joystick
Section titled “2. Create the Joystick”Add the joystick to your scene in the create() method:
export class GameScene extends Phaser.Scene { private joystick!: VirtualJoystick;
create() { // Create the virtual joystick with default settings this.joystick = new VirtualJoystick({ scene: this });
// ⚠️ IMPORTANT: Don't forget to add the joystick to the scene! this.add.existing(this.joystick); }}3. Handle Input
Section titled “3. Handle Input”Listen to joystick events to control your game:
create() { // ... joystick creation code ...
// Listen to movement this.joystick.on('move', (data) => { console.log('Joystick moved:', data.x, data.y); // data.x and data.y are between -1 and 1 });
// Listen to press this.joystick.on('press', () => { console.log('Joystick pressed'); });
// Listen to release this.joystick.on('release', () => { console.log('Joystick released'); });}Complete Example
Section titled “Complete Example”Here’s a complete example that moves a player sprite:
import { VirtualJoystick } from 'phaser-virtual-joystick';
export class GameScene extends Phaser.Scene { private joystick!: VirtualJoystick; private player!: Phaser.Physics.Arcade.Sprite;
preload() { // Load your player sprite this.load.image('player', 'assets/player.png'); }
create() { // Create player sprite this.player = this.physics.add.sprite(400, 300, 'player'); this.player.setCollideWorldBounds(true);
// Create virtual joystick this.joystick = new VirtualJoystick({ scene: this });
// ⚠️ IMPORTANT: Add joystick to scene this.add.existing(this.joystick);
// Handle joystick movement this.joystick.on('move', (data) => { // Move player based on joystick input this.player.setVelocity( data.x * 200, // Horizontal speed data.y * 200 // Vertical speed ); });
// Stop player when joystick is released this.joystick.on('release', () => { this.player.setVelocity(0, 0); }); }
update() { // Update joystick (required for smooth following behavior) this.joystick?.update(); }}Configuration Options
Section titled “Configuration Options”The joystick accepts a configuration object with the following options:
interface VirtualJoystickParams { scene: Phaser.Scene; // Required: The Phaser scene deadZone?: Partial<StyleConfig>; // Optional: Dead zone styling baseArea?: Partial<StyleConfig>; // Optional: Base area styling stick?: Partial<StyleConfig>; // Optional: Stick styling stickIcon?: Phaser.GameObjects.Text; // Optional: Icon on the stick bounds?: { // Optional: Activation area topLeft: { x: number; y: number }; bottomRight: { x: number; y: number }; }; enableWithoutTouch?: boolean; // Optional: Enable on non-touch devices}Style Configuration
Section titled “Style Configuration”Each visual component (deadZone, baseArea, stick) can be customized:
interface StyleConfig { alpha: number; // Transparency (0-1) strokeColor: number; // Stroke color (hex) strokeAlpha: number; // Stroke transparency (0-1) strokeWidth: number; // Stroke width in pixels radius: number; // Circle radius in pixels fillColor: number; // Fill color (hex)}Understanding the Values
Section titled “Understanding the Values”The joystick provides normalized values:
- X axis: -1 (left) to 1 (right)
- Y axis: -1 (up) to 1 (down)
- Center: (0, 0) when not touched
this.joystick.on('move', (data) => { if (data.x > 0.5) { // Moving right } else if (data.x < -0.5) { // Moving left }
if (data.y > 0.5) { // Moving down } else if (data.y < -0.5) { // Moving up }});Default Behavior
Section titled “Default Behavior”- Activation Area: Left half of the screen (with 20% top padding)
- Visual Style: Blue-themed with subtle transparency
- Dead Zone: 16px radius - no input registered in this area
- Base Area: 64px radius - maximum joystick movement range
- Stick: 40px radius - follows your finger with smooth following behavior
- Touch Only: Only works on touch devices by default
Touch Detection
Section titled “Touch Detection”The joystick automatically detects touch capability and only appears on devices that support it. On desktop browsers, the joystick will be hidden unless you set enableWithoutTouch: true.
Next Steps
Section titled “Next Steps”- Learn about advanced usage patterns
- Check out the API reference
- See customization options
Troubleshooting
Section titled “Troubleshooting”Joystick not appearing
Section titled “Joystick not appearing”- Make sure you called
this.add.existing(joystick) - Check if you’re on a touch device (or set
enableWithoutTouch: true)
Joystick not responding
Section titled “Joystick not responding”- Verify the touch is within the bounds area
- Check if there are interactive objects blocking the touch
Performance issues
Section titled “Performance issues”- Make sure to call
joystick.update()in your scene’s update method - Consider reducing the update frequency if needed